Restaurant waste is an important topic for business owners in the food industry to know more about.
Welcome to the ultimate guide on managing restaurant waste in the UK.
As a restaurant owner, understanding and efficiently managing waste is crucial not only for environmental sustainability but also for compliance with regulations and reducing costs.
In this guide, we explore the various aspects of restaurant waste, including its types, regulations, disposal methods, and best practices.
Table of Contents:
- What is Restaurant Waste?
- Restaurant Waste Terms You Might Not Know
- Types of Restaurant Waste
- Restaurant Waste Laws and Regulations in the UK:
- How to Manage Restaurant Waste:
- Restaurant Waste Disposal Methods:
- Interesting Facts and Statistics:
- Conclusion
What is Restaurant Waste?
Restaurant waste includes any materials generated during the operation of a restaurant that are no longer needed, ie wasted.
This includes food waste, packaging, paper products, plastic utensils, glass bottles, and more.
Understanding the composition of restaurant waste is the first step towards effective restaurant waste management.
Managing your restaurant’s waste benefits the environment.
Did you know that your food waste can and should actually be recycled?
Food waste can be so bad for the environment because it typically ends up in a general waste bin, where it is moved to a landfill and releases greenhouse gases like methane, contributing massively to climate change.
The second reason it’s so important is that it’s also the legal responsibility of restaurants in the UK to ensure that their waste is disposed of in a safe and responsible manner.
Restaurant Waste Terms You Might Not Know
Storage waste – waste that has been stored incorrectly so has expired or been contaminated.
Preparation waste – cut-offs, peels, skins, miscuts, spillages
Portion waste – food wastage from restaurants giving too large a portion to customers
Plate waste – leftover food on plates
Types of Restaurant Waste
Restaurant waste is diverse and encompasses various materials generated throughout the daily operations of a dining establishment.
Understanding the different types of waste is crucial for implementing effective management strategies and reducing environmental impact.
Here are the primary categories:
Food Waste
According to recent studies, food waste accounts for a significant portion of restaurant waste.
In the UK alone, it’s estimated that approximately 10.7 million tonnes of food waste are generated annually, with restaurants contributing a substantial portion to this figure.
Dry Mixed Recycling
Dry Mixed Recycling waste from restaurants usually consists of packaging materials like cardboard boxes, plastic wrappers, and containers that contribute to restaurant waste.
With the rise of takeaway and delivery services, the volume of packaging waste has increased significantly.
Did you know that Uber Eats, one of the most popular takeaway delivery services, has had massive growth from 2017; going from 80,000 supported restaurants in 2017 to 825,000 supported restaurants in 2022?
Restaurants also generate a lot of dry mixed recycling from menus, napkins, and disposable utensils that contribute to paper, plastic and cardboard waste.
Implementing paperless solutions, biodegradable & reusable options and promoting recycling can help reduce this type of waste.
General Waste
General waste in restaurants usually includes non-recyclable packaging, single-use plastics, and other non-biodegradable materials discarded during daily operations.
This waste category also includes food-soiled items such as greasy pizza boxes and miscellaneous items like broken equipment and outdated promotional materials.
Implementing strategies to minimise the generation of general waste, such as switching to eco-friendly packaging and promoting reusable alternatives, is essential for reducing the environmental impact of restaurant operations.
Glass Recycling
Glass recycling in restaurants involves the collection and processing of glass bottles and containers used in food and beverage service.
Typically, glass recycling in restaurants includes bottles from alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages, as well as glass jars from condiments and food ingredients.
These items are collected separately and transported to recycling facilities where they are sorted, cleaned, and processed into new glass products.
Implementing a glass recycling program in restaurants can significantly reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills, promote resource conservation, and contribute to a more sustainable food service industry.

Restaurant Waste Laws and Regulations in the UK:
In the UK, restaurant waste management is governed by various laws and regulations to ensure environmental protection and public health.
Key regulations include:
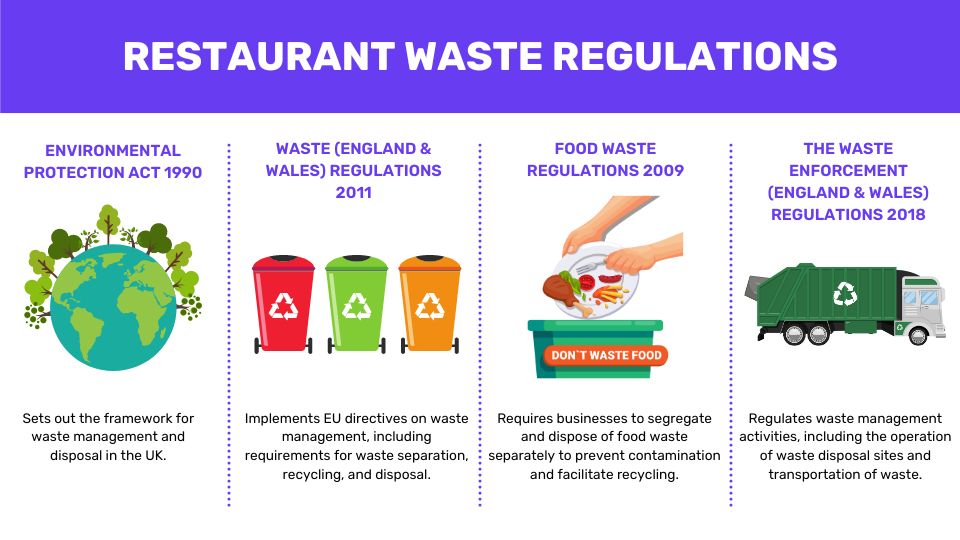
- Environmental Protection Act 1990:
Sets out the framework for waste management and disposal in the UK.
- Waste (England and Wales) Regulations 2011:
Implements EU directives on waste management, including requirements for waste separation, recycling, and disposal.
- Food Waste Regulations 2009:
Requires businesses to segregate and dispose of food waste separately to prevent contamination and facilitate recycling.
- The Waste Enforcement (England & Wales) Regulations 2018
Regulates waste management activities, including the operation of waste disposal sites and transportation of waste.

How to Manage Restaurant Waste:
There are many ways to reduce your restaurant’s waste!
Read our top tips below to find out how you can cut down on your commercial waste and help out the planet in the process.
Reduce
Minimising waste generation begins with optimising portion sizes to match customer preferences and reduce excess food waste.
Implementing efficient inventory management systems helps prevent overordering of ingredients, minimising food spoilage and waste.
Additionally, offering customisable menu options and sizing allows customers to tailor their orders, reducing the likelihood of uneaten food being discarded.
Reuse
Encouraging the use of reusable utensils, containers, and tableware promotes sustainability by reducing reliance on single-use plastic and packaging.
Restaurants can offer incentives such as discounts or loyalty rewards to customers who bring their reusable cups or containers.
Additionally, implementing a deposit-return system for reusable items encourages customers to return them for reuse, further reducing waste.
Recycle
Establishing a comprehensive recycling program enables restaurants to divert recyclable materials such as paper, cardboard, plastic, and glass from landfill disposal.
Providing clearly labelled recycling bins in dining areas and kitchen facilities encourages staff and customers to separate recyclables from general waste.
Partnering with local recycling facilities ensures proper processing and disposal of recyclable materials.
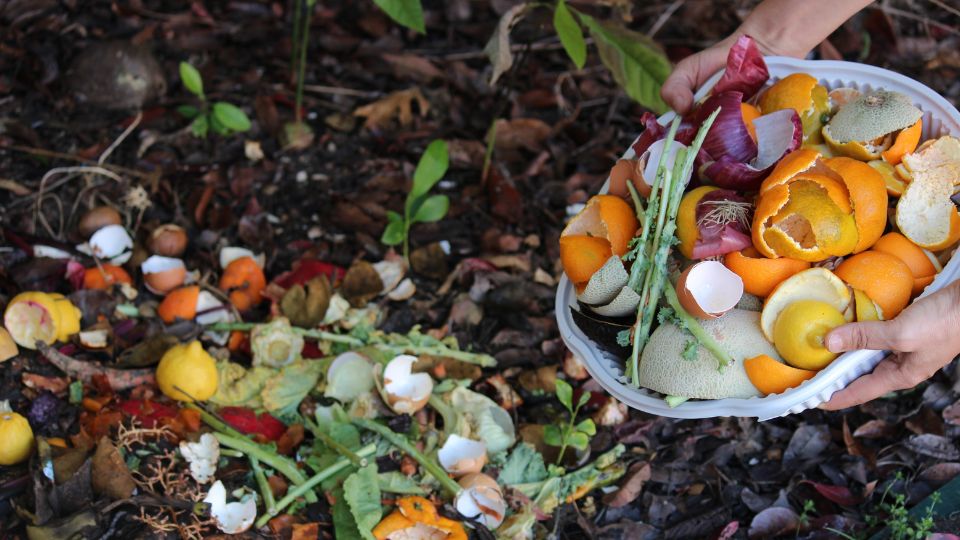
Compost
Setting up composting bins for organic waste allows restaurants to divert food scraps, vegetable peelings, and other biodegradable materials from landfill disposal.
Composting not only reduces waste volume but also produces nutrient-rich compost that can be used to enrich soil in gardens or landscaping projects.
Restaurants can use the compost produced on site or donate it to local community gardens or urban farms.
Waste Audits
Conducting regular waste audits helps identify areas for improvement in waste management practices and track progress towards waste reduction goals.
By analysing waste streams and identifying sources of waste generation, restaurants can implement targeted strategies to minimise waste and optimise resource efficiency.
Engaging staff members in waste audit processes creates a culture of sustainability, and encourages collective efforts towards waste reduction and environmental stewardship for restaurants and other businesses.

Restaurant Waste Disposal Methods:
Landfill
Landfill disposal involves transporting waste to designated landfills for burial, where it undergoes decomposition over long periods.
However, landfill disposal is associated with significant environmental drawbacks, including soil and water contamination, greenhouse gas emissions, and habitat destruction.
The accumulation of organic waste in landfills generates methane, a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
Therefore, landfill disposal should be avoided whenever possible, and efforts should be made to minimise the volume of waste sent to landfills through waste reduction, recycling, and composting initiatives.
Recycling
Recycling involves the collection, processing, and transformation of waste materials into new products.
Recycling materials such as paper, cardboard, plastic, and glass conserves natural resources, reduces the need for raw materials, and minimises energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with manufacturing processes.
By diverting recyclable materials from landfills, recycling helps mitigate environmental impact and promotes a circular economy.
Implementing effective recycling programs in restaurants encourages sustainable waste management practices and supports the transition to a more environmentally friendly food service industry.
Composting
Composting is a natural process that converts organic waste, such as food scraps, yard trimmings, and paper products, into nutrient-rich compost.
Composting not only diverts organic waste from landfills but also produces a valuable soil amendment that can improve soil health and fertility.
By composting organic waste, restaurants can reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with landfill decomposition, conserve landfill space, and support sustainable agriculture and landscaping practices.
Implementing on-site composting systems or partnering with local composting facilities enables restaurants to close the loop on organic waste management and promote environmental sustainability.
Waste-to-Energy
Waste-to-energy (WTE) technologies convert organic waste into usable energy through processes such as incineration or anaerobic digestion.
Incineration involves burning organic waste at high temperatures to generate heat and electricity, while anaerobic digestion breaks down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas that can be used for energy production.
WTE facilities help reduce reliance on fossil fuels, minimise landfill methane emissions, and contribute to renewable energy generation.
While WTE can be a viable option for managing organic waste, it’s essential to consider environmental and health implications and prioritise waste reduction and recycling efforts as the preferred waste management strategies.
How often should restaurant bins be emptied?
You should empty your restaurant bins every single day.
Restaurants should empty their internal bins every day (or numerous times if it’s busy) to prevent any bacteria from contaminating kitchen surfaces and other food preparation locations.
These internal bins should be emptied into your larger commercial wheelie bins outside your restaurant ready for collection – typically on a weekly or fortnightly schedule.

Interesting Facts and Statistics:
- A single restaurant can produce up to 25,000-75,000 pounds (that’s 11,339-34,019kg) every single year! That’s the equivalent of 11-34 horses!
- We waste one billion tonnes of food every single year across the world, this is in a time of extreme food poverty for least-developed countries (LDCs) where access to proper nutrition is extremely difficult.
- One third of all food produced globally is lost or wasted.
- In the UK, 9.5 million tonnes of food waste are generated every year, with 1.1 million tonnes (12%) coming from the restaurant and hospitality sector alone.
- The food waste in the UK costs us £19 billion a year.
- The food waste from the UK alone is associated with 25 million tonnes of greenhouse gas emissions.
- 6.4 million tonnes of food waste could have been eaten, which is the equivalent of 15 billion meals!
- As the amount of food waste increases, so does food insecurity. Not having proper waste management has a direct effect on those least fortunate (over 800 million people).
- 17% of a customer’s meal in a restaurant is left uneaten, and 55% of leftovers in restaurants are completely edible.

Conclusion
Effective management of restaurant waste is not only essential for environmental sustainability but also for reducing costs and complying with regulations.
By implementing strategies to reduce, reuse, recycle, and compost waste, restaurant owners can minimise their environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Remember, every effort counts towards making a positive impact on the environment and the bottom line of your restaurant business.
Start implementing these waste management practices today to make a difference.








